Pregnancy Basics
Lasting approximately 40 weeks (280 days), pregnancy is the condition of carrying a developing fetus in the uterus. It is the result of a sperm fertilizing a woman’s egg.
 Ovulation is the release of an egg from the ovaries. Normally, women who have not yet undergone menopause will ovulate once a month. The egg then travels through the fallopian tube toward the uterus. When sperm reaches the egg, normally in the fallopian tube, fertilization occurs. The fertilized egg continues to move towards the uterus. Once within the uterus, it implants itself in the uterine wall and begins to develop into an embryo.
Ovulation is the release of an egg from the ovaries. Normally, women who have not yet undergone menopause will ovulate once a month. The egg then travels through the fallopian tube toward the uterus. When sperm reaches the egg, normally in the fallopian tube, fertilization occurs. The fertilized egg continues to move towards the uterus. Once within the uterus, it implants itself in the uterine wall and begins to develop into an embryo.  Pregnancy can cause a number of noticeable changes in a woman’s body. Among the earliest changes is the absence of menstruation. This is often one of the first signs of pregnancy. During early pregnancy, (the first three months or first trimester), a woman may also notice symptoms such as fatigue, nausea and vomiting (morning sickness), and enlarging or tender breasts. Women who suspect they may be pregnant can verify their condition with a pregnancy test.
Pregnancy can cause a number of noticeable changes in a woman’s body. Among the earliest changes is the absence of menstruation. This is often one of the first signs of pregnancy. During early pregnancy, (the first three months or first trimester), a woman may also notice symptoms such as fatigue, nausea and vomiting (morning sickness), and enlarging or tender breasts. Women who suspect they may be pregnant can verify their condition with a pregnancy test.
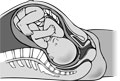
As pregnancy progresses to the second (weeks 13 to 24) and third trimesters (week 25 to delivery), a woman experiences a wide variety of additional symptoms, the most prominent being an expanding abdomen. Symptoms also may include leg cramps, muscle soreness, heartburn and hemorrhoids. These potential symptoms and changes occur as a result of pregnancy hormones as well as effects from the continuing fetal growth.
By the end of the first trimester the fetus is about 3 inches (76 millimeters) long and weighs about half an ounce (14 grams). By the end of the third trimester, the average fetus is about 20 inches (508 millimeters) long and weighs about 7 pounds (3 kilograms). Pregnancy ends with labor and delivery.
Physicians usually estimate the time a baby will be born (estimated due date [EDD]) by subtracting three months from the last menstrual period month and adding seven days to the last menstrual period day. This is approximately 40 weeks.
Although pregnancy can cause a number of changes in a woman, there is no way to predict which symptoms a woman will experience. Each pregnancy is different, even subsequent pregnancies in the same woman. Women who experience discomforts associated with pregnancy should discuss them with their obstetrician–gynecologist (ObGyn). Physicians can recommend a number of safe and effective treatment methods for pregnancy–related discomfort. In addition, pregnant women should always discuss prescription and over–the–counter medications (e.g., antacids, decongestants) with their ObGyn before taking them.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home